√無料でダウンロード! sinuses of valsalva echo 201460-Sinus of valsalva measurement echo
Aneurysm of the Sinus of Valsalva In aneurysm of the sinus of Valsalva (congenital aortic sinus aneurysm), there is a gradual downward protrusion of the aneurysm into a lower pressure cardiac chamber and eventually rupture Most of the aneurysm arises from the right coronary sinus (80%) and less frequently from the noncoronary cusp (%)Sep 21, 16 · Sinus of valsalva anatomy Any one of the pouches of the aorta and pulmonary artery which are located behind the flaps of the semilunar valves and into which the blood in its regurgitation toward the heart enters and thereby closes the valves called also aortic sinus The sinuses of valsalva also known as aortic sinuses are the anatomic spacesMar 10, 15 · A sinus of Valsalva aneurysm (SOVA) is an enlargement of the aortic root area between the aortic valve annulus and the sinotubular ridge 1 In a normal heart, the left and right sinus each contain their respective coronary artery ostia, whereas the posterior sinus is a noncoronary sinus

The Role Of Echocardiography In Aortic Valve Repair Vanoverschelde Annals Of Cardiothoracic Surgery
Sinus of valsalva measurement echo
Sinus of valsalva measurement echo-Jun 05, 16 · Localized dilatation of one or more sinuses of Valsalva is called sinus of Valsalva aneurysm Echo assessment of aortic dilatation Aortic dilatation can occur in more than one site, so for an aortic assessment it is important to measure the aortic dimensions in as many sites as possible ( Fig 262 )Sinus of Valsalva aneurysms can be well visualized with transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) provided that acoustic win dows are adequate;




Transcatheter Closure Of Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva To Left Ventricle Manuel Da Lahiri A George Ok Ann Pediatr Card
Dilated aortic root It means the part of the aorta coming out of the left ventricle is dilated and the sinuses of valsalva which make op the area including the valve are Read More 90,000 US doctors in 147 specialties are here to answer your questions or offer you advice, prescriptions, and more Get help nowAortic Root ZScores Use this calculator to determine zscores for the aortic valve and aortic root (sinus of Valsalva), using data from Boston Children's Hospital Per the authors, the technique used is "Aortic annulus and root diameters were measured from parasternal longaxis images, with the aortic root diameter taken as the maximumAbstract—The association of sinuses of Valsalva dilatation and aortic regurgitation with hypertension is disputed, and few data are available in populationbased samples We explored the relations of sinuses of Valsalva dilatation and aortic regurgitation to hypertension and additional clinical and echocardiographic data in 96 hypertensive and 361
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsSinus of Valsalva aneurysms are rare entities Unique complications associated with sinus of Valsalva aneurysms make them different from traditional aortic root aneurysms Established guidelines on the diagnosis and management of sinus of Valsalva aneurysms are lackingAbstract Twodimensional echocardiography is increasingly used to measure aortic root dimensions, which provide prognostic information in aortic regurgitation and the Marfan syndrome Aortic root dilatation is currently detected by nomograms based on Mmode echocardiographic data Aortic root diameters measured by 2dimensional echocardiography at the anulus, sinuses of Valsalva
Terdjman M, Bourdarias JP, Farcot JC, et al Aneurysms of sinus of Valsalva twodimensional echocardiographic diagnosis and recognition of rupture into the rightMoustafa S, Mookadam F, Cooper L, et al Sinus of Valsalva aneurysms47 years of a single center experience and systematic overview of published reports Am J Cardiol 07;Oct 18, 16 · sinus of Valsalva with any of the chambers RA and RV were of normal size TEE revealed same findings as in 2D echo, but both the right and left sinus of valsalva were seen dilated with the right coronary cusp (RCC) seen dissecting into the IVS with a nodular calcification in the vicinity of AoV as shown in Figure 2 Aortogram



Plos One Echocardiographic Diagnosis Of Rare Pathological Patterns Of Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm




Rare Presentation Of A Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Case
Background Rupture of Sinus of Valsalva (rSOV) is a rare and potentially lifethreatening condition often misdiagnosed Percutaneous device closure has been replacing surgical repair as a treatment of choice However, longterm outcome is poorly documented Methods Echo database (0119) was searched for patients >16y with rSOVSinuses of Valsalva The sinuses of Valsalva are outward pouches within the aortic root where the coronary arteries arise from They act as a reservoir of blood to supplement the coronaries during diastole During systole, the outward pouches act as support for the leaflet cusps Leaflet Cusps The aortic valve is composed of 3 leafletsJul 01, 15 · Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm (SVA) is a rare congenital heart malformation of one or more of the aortic sinuses, consisting of a dilation that when unruptured is usually asymptomatic but when ruptured presents with progressive exertional dyspnea, fatigue, chest pain and that can lead to congestive heart failure if left untreated




Aneurysm Of Sinus Of Valsalva Complications Wikidoc




Distribution Of The Types Of Ruptured Sinuses Of Valsalva In The Study Download Scientific Diagram
The Sinus of Valsalva was measured incorrectly because the sinus was not measured at the maximum curvature of the right and noncoronary aortic sinuses This measurement was taken too close to the aortic annulus and not at the maximum diameter The Echo Accreditation process includes the submission of aortic stenosis case studies to theBackground Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm (SVA) is a rare cardiac anomaly which has potential for spontaneous rupture into other cardiac chambers or the pericardial space (depending on its location) A ruptured SVA has a very poor prognosis with high morbidity and mortality The development of a shunt between the sinus of Valsalva and rightsided cardiac chambers resultsCullen S et al Transcatheter closure of a ruptured aneurysm of the sinus of valsalva Br Heart J 1994;–80




Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Diagnosis By Community Echocardiography In Echo Research And Practice Volume 7 Issue 4
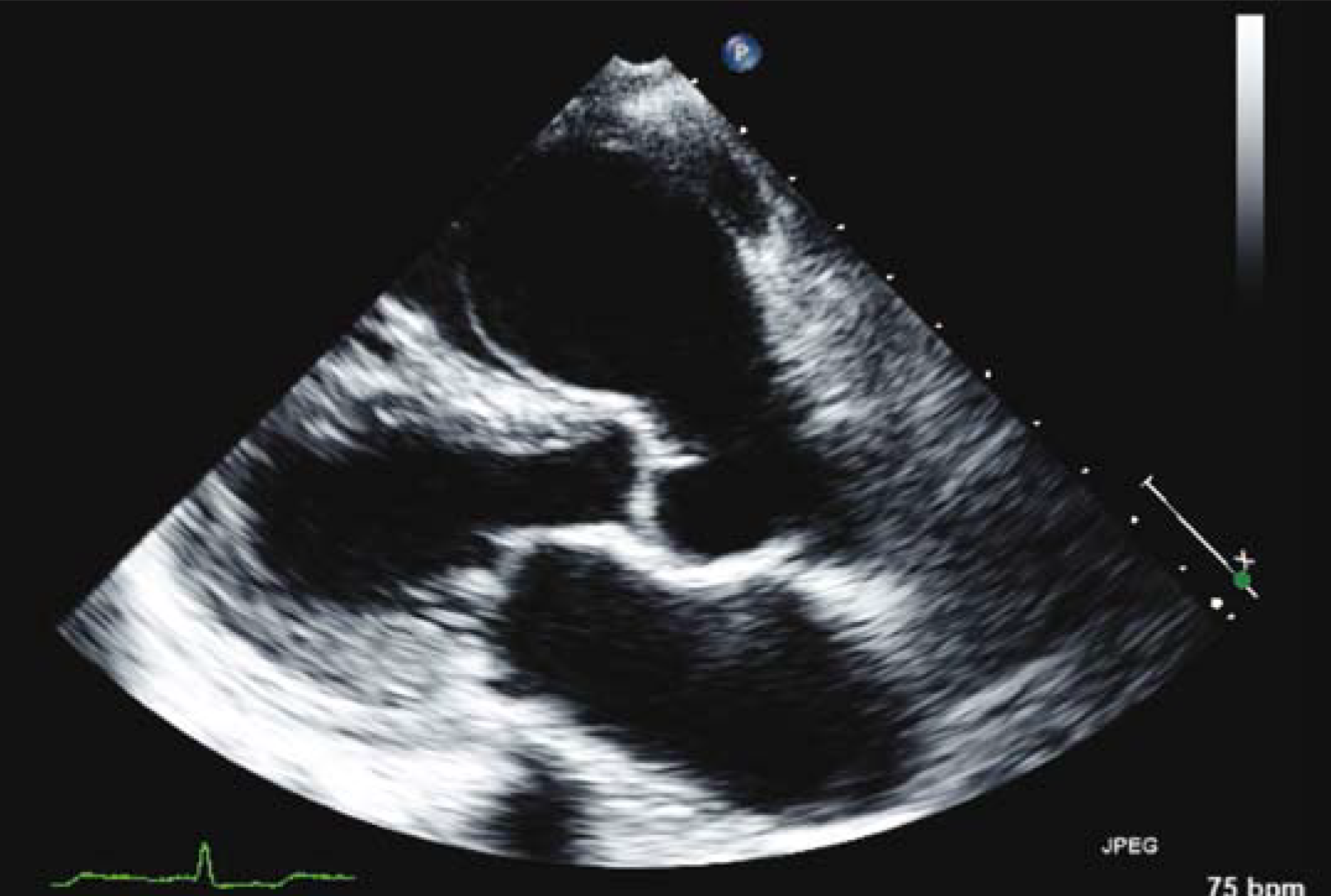



Aneurysm Of The Sinus Of Valsalva The British Journal Of Cardiology
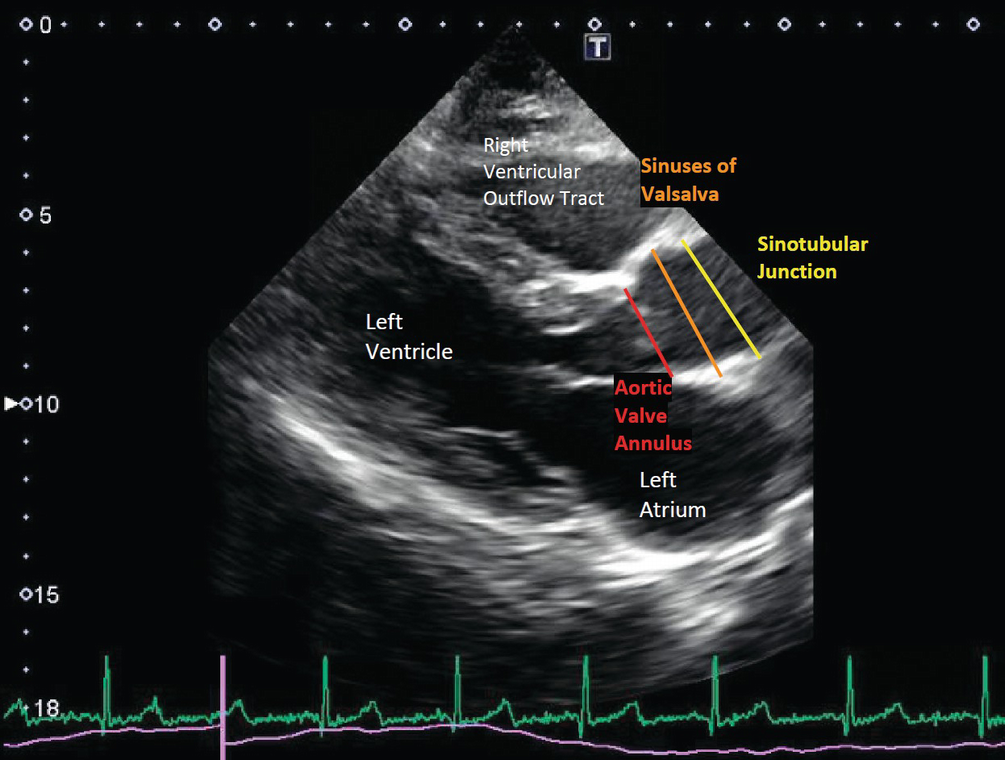
An aneurysm of the sinus of the Valsalva is often the result of a congenital heart defect Typically, there are no signs of an aneurysm in this area, and it is often not discovered until it either ruptures or is found during a scan, usually a CT scan or echocardiogram , for another issueThe sinus of Valsalva was measured as cusptocommissure where all three aortic valve cusps were evenly represented The sinotubular junction was measured at the narrowest level in the transition of the aortic root to the ascending aorta Measurements of the ascending and descending aortaEcho dhflp Hi,I'm a 53 year old male with BSA of 8 and the following echo results "There was a minimal pericardial effusion,without hemodynamic compromise" 1 What's the acceptable amount of fluid around the heart in cc and is the above finding within this acceptable amount of fluid around the heart and therefore a normal finding?




The Role Of Echocardiography In Aortic Valve Repair Vanoverschelde Annals Of Cardiothoracic Surgery




Figure 1 From Aneurysm Of Sinus Of Valsalva Semantic Scholar
Left sinus aneurysms are rare (less than 5%) Congenital aneurysms are more prevalent than acquired aneurysms, and most of these involve the noncoronary and right sinus of Valsalva (99%) Acquired sinus of Valsalva aneurysms may arise from any one of or involve all three sinuses Sinus of Valsalva aneurysms are associated with Marfan syndromeSinus of Valsalva aneurysm is most easily diagnosed by echocardiography and requires surgical treatment The bulbous portion houses the aortic valves and the aortic annulus, and gives origin to the coronary arteries These are the only set of branching4 Well, I know generally, the mean normal value for aortic root annulus is 26cm and for the proximal ascending aorta is 29cm,but what




Valsalva Sinus Aneurysms Findings At Ct And Mr Imaging Radiographics




Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva An Unusual Cause Of Heart Failure Dubey L J Cardiovasc Echography
The thoracic aorta can be subdivided ito the aortic root (including the aortic annulus, aortic valve, and sinuses of Valsalva), the ascending aorta, the aortic arch, and the descending aorta Spontaneous echo contrast and thrombus can be seen in the false lumenMar 25, 14 · Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm (SVA) is a rare cardiac anomaly that can be congenital or acquired We report 2 cases of SVA The first case involves a 59‐year‐old male presenting with frequent syncope Echocardiogram revealed a large right SVA obstructing the right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT)3Usually does echo underestimates or overestimates measurement of aortic root at sinus of valsalva?



Plos One Echocardiographic Diagnosis Of Rare Pathological Patterns Of Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm
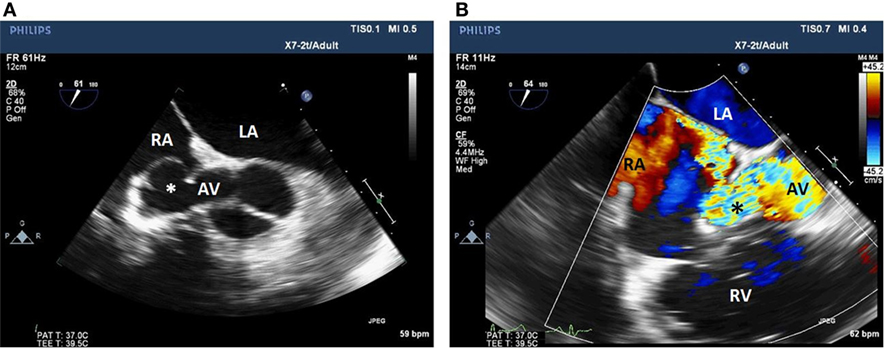



Frontiers Incidental Finding Of An Aorto Right Atrial Fistula In A Patient Undergoing Repair Of A Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Medicine
Dr Ian Nicholson, Cardiac Surgeon at Westmead Children's Hospital, talks about Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm repairPresentation delivered at the Structural HeaA 2cm aneurysm of the right sinus of Valsalva was documented in a patient with a prosthetic aortic valve The Mmode findings differed from prior reports and mimicked those of aortic root dissection or a catheter placed in the right ventricular outflow tract Twodimensional echocardiograms readily distinguished the aneurysm of the right sinus of Valsalva from theDec 01, · Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm is a rare abnormality (population incidence 009%) that occurs due to a weakening of the layers of the aortic wall (principally the aortic media) This may be due to a congenital abnormality in the aortic wall or may be acquired following bacterial endocarditis or connective tissue disorders




Classical Windsock Deformity Of Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva An Unusual Appearance On Transthoracic Echocardiography Bmj Case Reports
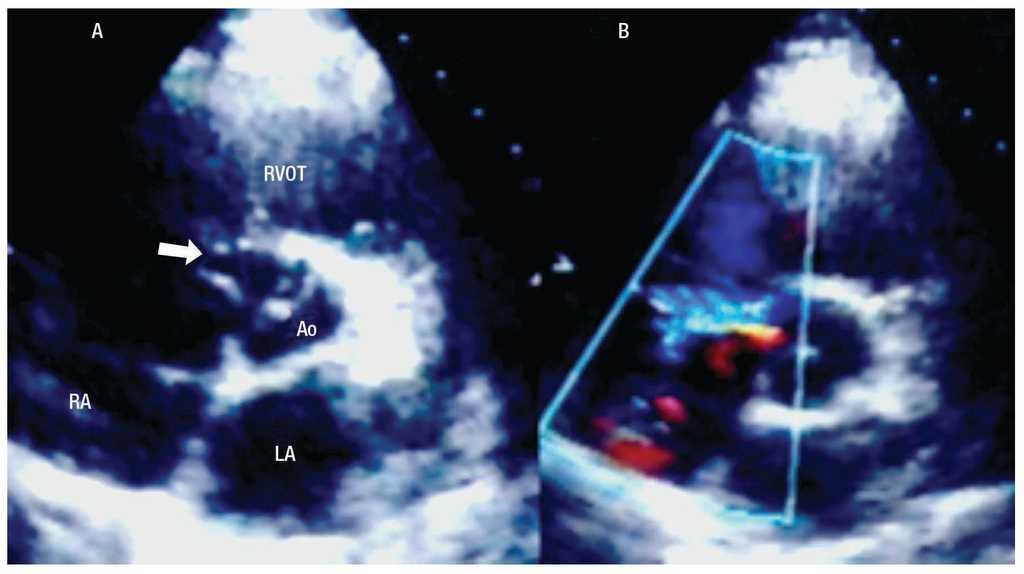



Spontaneous Rupture Of An Aneurysm Of The Sinus Of Valsalva Into The Right Atrium Associated With An Atrial Septal Aneurysm Archivos De Cardiologia De Mexico
What's the upper normal limit for aortic root at sinus of valsalva in the above person by echo and mri?Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm is a rare cardiac anomaly usually detected in the third or fourth decade of life This lesion is more frequent in males and more commonly arises from the right coronary (77%) followed by noncoronary (23%) and, sometimes, the left coronary sinus of Valsalva Congenital defect of the aortic media is the main etiology of these aneurysmsOct 15, 12 · Sinuses of Valsalva diameter was measured by American Society of Echocardiography convention in normalweight, nonhypertensive, nondiabetic individuals ≥15 years old without aortic valve disease from clinical or populationbased samples
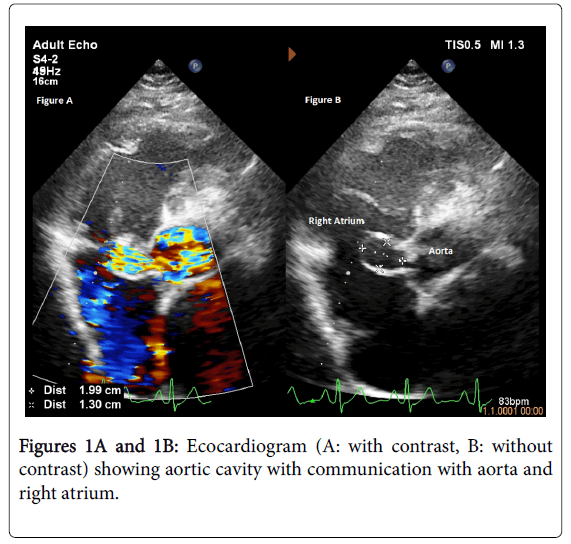



A Case Of Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Mimicking Ventricular Septal Defect




An Unusual Cause For Unruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Sciencedirect
The sinus of valsalva aneurysm in all patients was made on the basis of the colour flow imaging pattern and Doppler spectra showing a continuous flow from the aorta to the respective right heart chambers Hence, although 2D echo imaging can establish the diagnosis of a sinus of valsalva aneurysm, colour flowObjective To evaluate the value of echocardiography in the diagnosis of different pathological patterns of sinus of Valsalva aneurysms (SVAs) Methods Echocardiographic features and surgical findings of 212 consecutive patients with SVAs treated in the last 17 years () at the Union Hospital of Huazhong University of Science and Technology were compared and analyzedThe sinuses of Valsalva, also known as aortic sinuses, are the anatomic spaces at the aortic root bounded internally by the aortic valve leaflets and externally by outward bulges of the aortic wall The normal sinus diameter upper limit is usually taken as 40 mm (with some publications suggesting 36 mm for females) 1




Sinus Of Valsalva Rupture With Dissection Into The Interventricular Septum Circulation




Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysms Review Of The Literature And An Update On Management Weinreich 15 Clinical Cardiology Wiley Online Library
A tenyear review of ruptured sinus of valsalva clinicopathological and echodoppler features Singapore Med J 01;;Aneurysm of the aortic sinus, also known as the sinus of Valsalva, is a rare abnormality of the aorta, the largest artery in the body The aorta normally has three small pouches that sit directly above the aortic valve, and an aneurysm of one of these sinuses is a thinwalled swelling Aneurysms may affect the right, noncoronary, or rarely the left coronary sinus These aneurysms may not cause any symptoms but if large can cause shortness of breath, palpitations or blackouts Aortic sinus aneurFeldman DN, Roman MJ Aneurysms of the sinus of valsalva Cardiology 06;;




View Image




Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysms A State Of The Art Imaging Review Journal Of The American Society Of Echocardiography
May 26, 14 · Aneurysm of sinus of Valsalva is a rare anomaly which arises from a congenital defect of the aortic media or due to damage caused by bacterial endocarditis It is more prevalent in men and people of Asian descent1 Ruptured sinus of Valsalva (RSOV) is a relatively uncommon cause of acute haemodynamic worsening which is usually seen in youngaged or middleagedMar 31, 13 · TwoDimensional Echo Reference Values for the Aortic Root Look up reference values— adjusted for age, gender, and body size— for the aortic root (aortic valve and sinus of Valsalva) using data published in the American Journal of Cardiology, 12 Select gender, enter values for height and weight and click "update" to generate links to theSinus of Valsalva aneurysm A sinus of Valsalva aneurysm refers to abnormal dilatation of the sinus of valsalva and is a cause of thoracic aortic dilatation Sinus of Valsalva aneurysms arise from one of the aortic sinuses They are either congenital or acquired




Reticent Uneventful Rupture Of Right Coronary Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Into Right Ventricle Heart Lung And Circulation
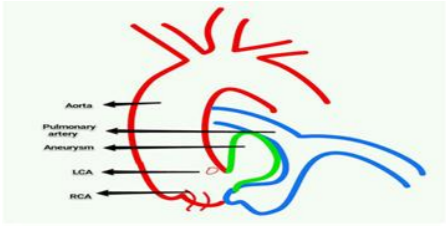



Unruptured Left Coronary Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Causing Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction Following Coronary Re Implantation Surgery Case Report Arc Journal Of Clinical Case Reports
Aug 13, 13 · One hundred twelve subjects aged –69 years were enrolled The aortic diameters (cm) determine by the aforementioned two guidelines showed significant difference Measurements were larger in 05 ASE guideline at aortic annuls, sinuses of Valsalva, and sinotubular junction level, but smaller at ascending aortic level with 23mm of differencesMar 30, 13 · Data Input Form Zscores of the aortic root (aortic annulus, sinuses of Valsalva, sinotubular junction, and ascending aorta) are commonly reported for conditions such as Marfan syndrome, bicuspid aortic valve, and Kawasaki disease This calculator consolidates the reporting of zscores and reference ranges for the aortic root, based onOct 01, 06 · The echocardiogram revealed enlargement of the right chambers and right coronary sinus of Valsalva Both contrast and colorDoppler techniques showed shunting from the sinus of Valsalva with the typical "wind sock" appearance into the right ventricle 1–7 and, passing through the tricuspidal leaflets, into the right atrium ( Fig 1 A,B)
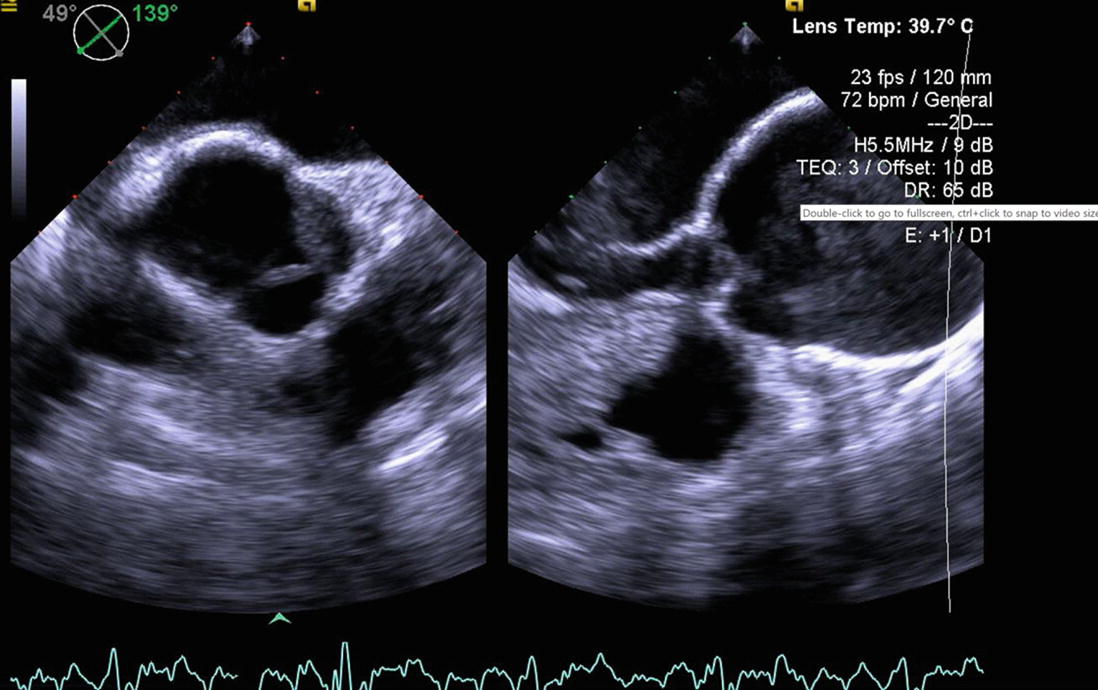



Annulo Aortic Ectasia And Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Springerlink




Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysms Circulation
However, transesophageal Sinus of Valsalva Aneurysms Assessment With Cardiovascular MRI Edward T D Hoey1,2 Arulnithy Kanagasingam3 Mohan U Sivananthan2,3 Hoey ETD, Kanagasingam A, Sivananthan MUA sinus of Valsalva aneurysm (SVA) is a rare congenital anomaly where there is dilatation of a single sinus of Valsalva which is a result of congenital weakening or absence of the media in one of the aortic sinuses Under the continued strain of aortic pressure, the weakened sinus gradually dilates and eventually forms an aneurysm



Www Ajronline Org Doi Pdf 10 2214 Ajr 09 3570




Transcatheter Closure Of Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva To Left Ventricle Manuel Da Lahiri A George Ok Ann Pediatr Card




How To Master Aortic Measurements With These 5 Techniques




Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Rupture Associated With A Ventricular Septal Defect The Importance Of Multi Angle Assessment By Intraoperative Transesophageal Echocardiography Journal Of Cardiothoracic And Vascular Anesthesia




Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm With Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction Circulation




How To Master Aortic Measurements With These 5 Techniques




Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm
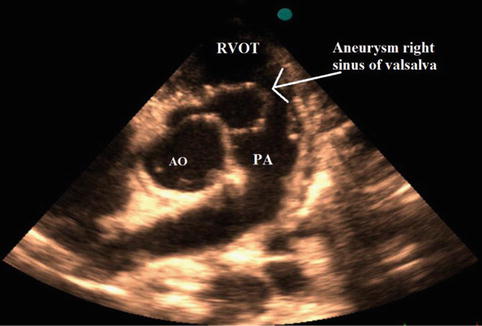



Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm And Fistula Springerlink




Transcatheter Closure Of Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm In A Pregnant Woman Sciencedirect




Figure 1 From Bicuspid Aortic Valve An Unusual Cause Of Aneurysm Of Left Coronary Sinus Of Valsalva Semantic Scholar



2




Transcatheter Closure Of Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva To Left Ventricle Manuel Da Lahiri A George Ok Ann Pediatr Card




Successful Device Closure Of A Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Presenting With Acute Heart Failure Bmj Case Reports
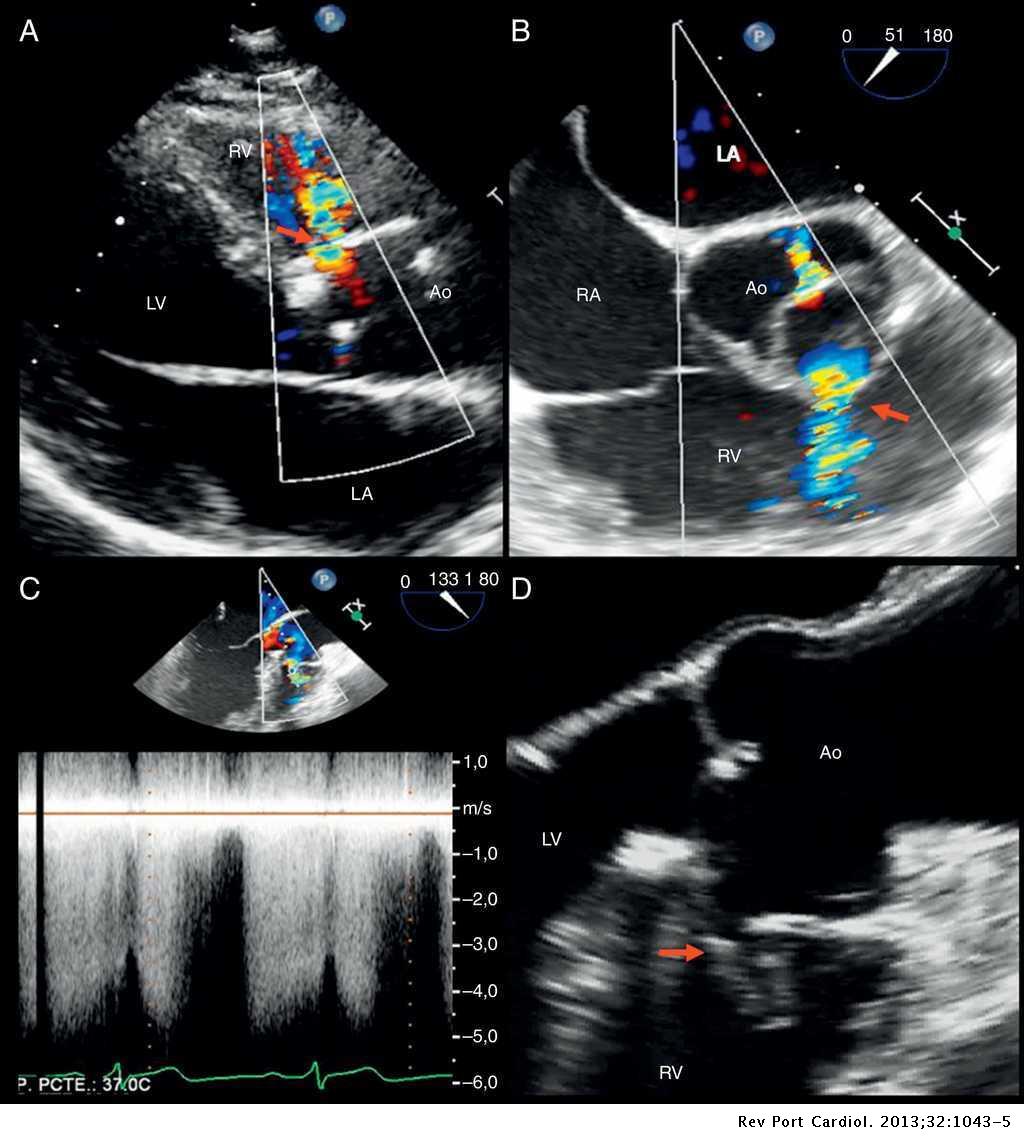



Echocardiographic Diagnosis Of Ruptured Right Sinus Of Valsalva Revista Portuguesa De Cardiologia English Edition




Valsalva Sinus Aneurysms Findings At Ct And Mr Imaging Radiographics




Aneurysm Of Sinus Of Valsalva An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Aortic Dimensions By Multi Detector Computed Tomography Vs Echocardiography Sciencedirect




Diagnosis And Management Of A Rare Case Of Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Into The Right Atrium



Unruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Dissecting Into Interventricular Septum A Windsock In The Heart Medcrave Online




Rupture Of Sinus Of Valsalva With Endocarditis And Aortic Root Abscess




Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm A Rare Cause Of Dyspnea



Ispub Com Ijc 8 2



Imaging Of The Aorta Springerlink




2d Echo Plax View Demonstrating Aneurysm Of Sinus Of Valsalva Download Scientific Diagram




Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva An Unusual Cause Of Heart Failure Dubey L J Cardiovasc Echography




Aneurysm Of Sinus Of Valsalva Wikipedia




Giant Unruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm An Unusual Cause Of Aortic Regurgitation Heart




Infective Endocarditis Of Right Sinus Valsalva Aneurysm Youtube



1



Echocardiographic Diagnosis Of Rare Pathological Patterns Of Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm




Aneurysm Of Sinus Of Valsalva Ruptured In The Right Ventricle Youtube




Two Different Presentations Of Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Patel 14 Echocardiography Wiley Online Library



Www Ecronicon Com Eccy Pdf Eccy 05 Pdf




A Spectrum Of Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm From The Young To The Old Mcgregor 17 Echocardiography Wiley Online Library




Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Diagnosis By Community Echocardiography In Echo Research And Practice Volume 7 Issue 4




Xmlinkhub
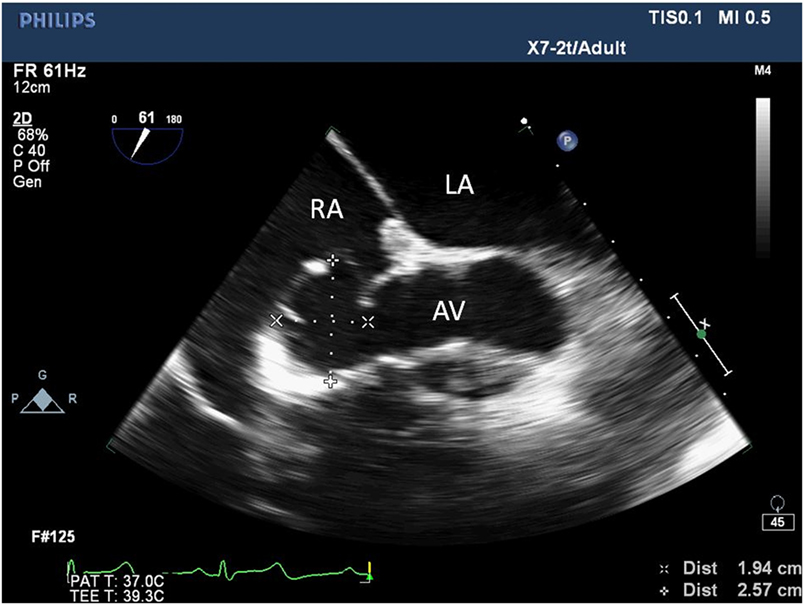



Frontiers Incidental Finding Of An Aorto Right Atrial Fistula In A Patient Undergoing Repair Of A Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Medicine



Ruptured Coronary Sinus Of Valsalva In The Setting Of A Supracristal Ventricular Septal Defect The Western Journal Of Emergency Medicine




A Rare Acute Right Heart Failure Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Into The Right Atrium



1



1
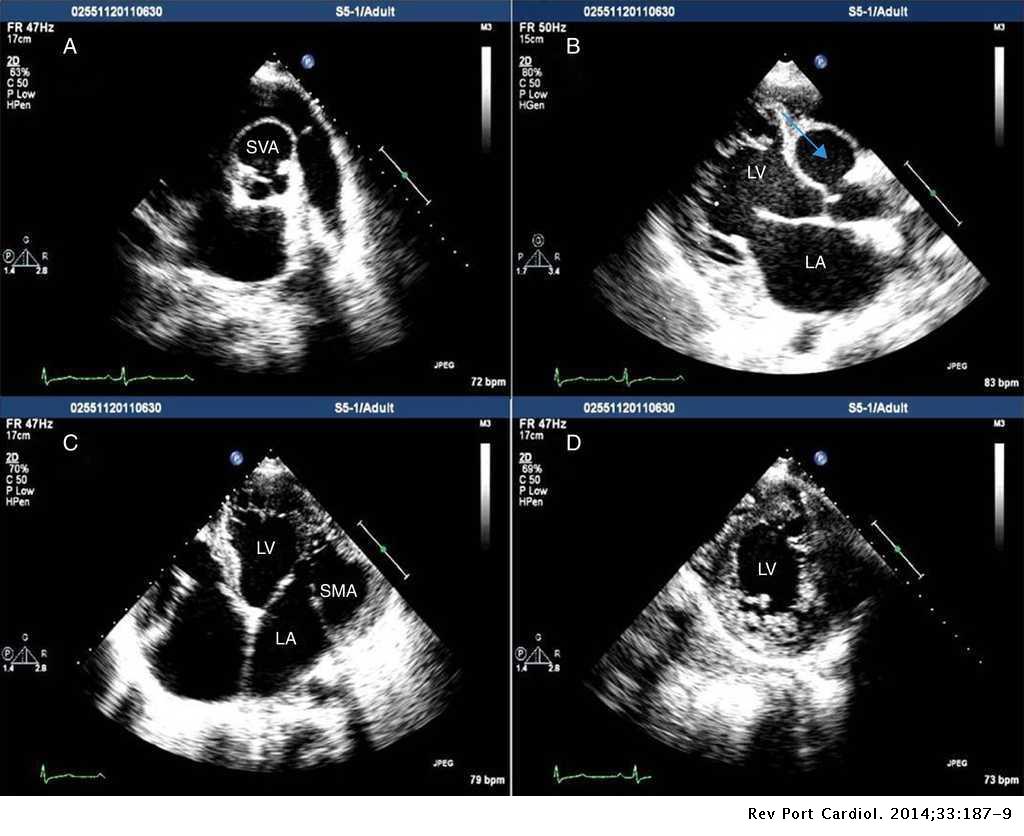



Aneurysm Of The Right Sinus Of Valsalva Dissecting Into The Interventricular Septum Submitral Aneurysm And Left Ventricular Non Compaction Three Rare Diseases In The Same Patient Revista Portuguesa De Cardiologia English Edition




Transcatheter Closure Of Giant Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Circulation




Multiple Ruptured Aneurysm Of Left Sinus Of Valsalva A Rare Entity Sarupria A Kapoor Pm Kiran U Hote M Ann Card Anaesth




Aneurysm Of Sinus Of Valsalva Wikipedia




Transthoracic Echocardiography Of Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Download Scientific Diagram
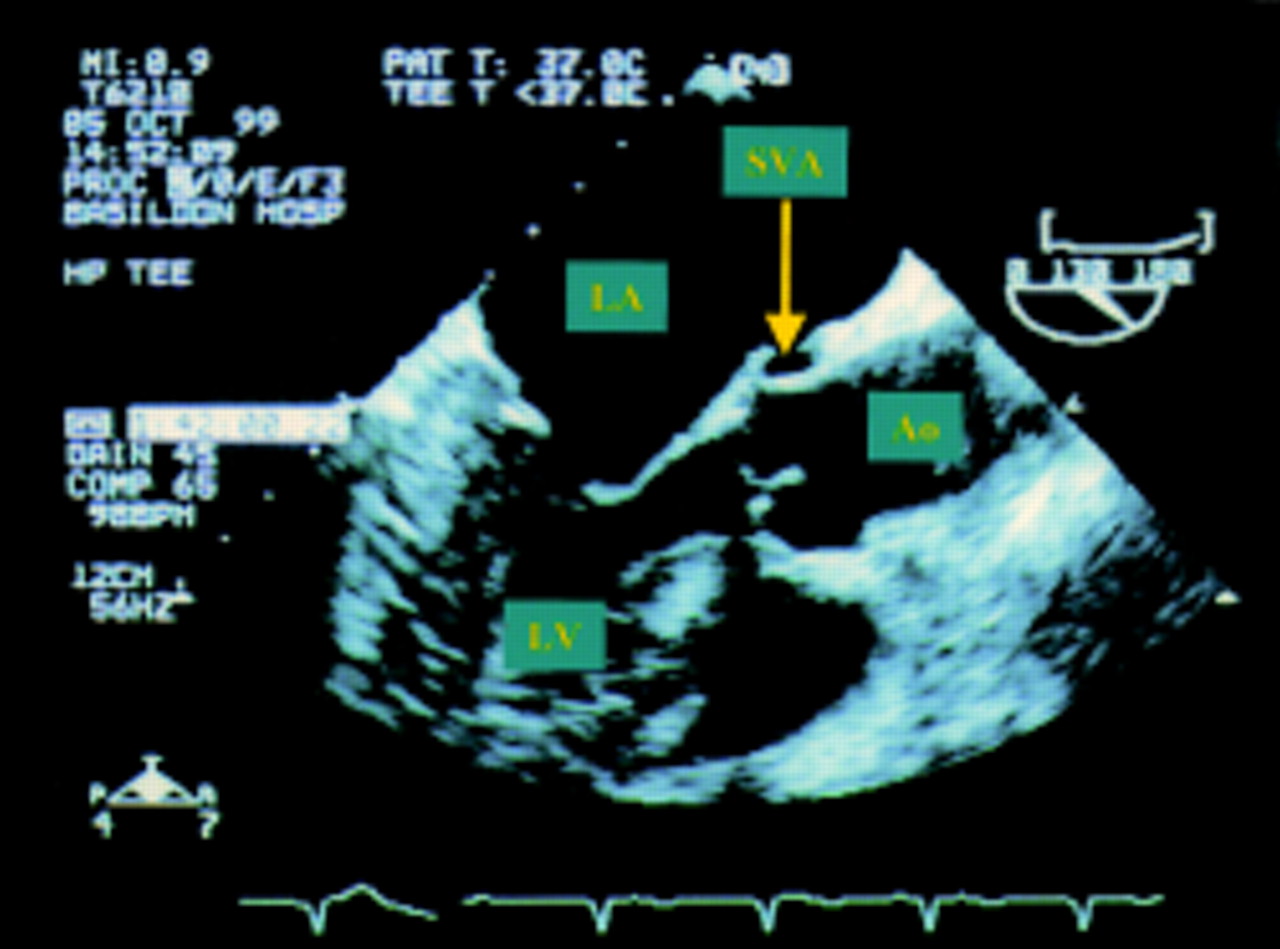



Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Rupture Into The Left Atrium Heart




Spontaneous Rupture Of Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Presenting As Perivalvular Hematoma Sharma A Yedlapati N Bob Manuel T Woods T Donovan D Ibebuogu Un J Cardiovasc Echography




Rupture Of Sinus Of Valsalva With Endocarditis And Aortic Root Abscess




Multiple Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysms A Triple Whammy Of Troubles Sciencedirect
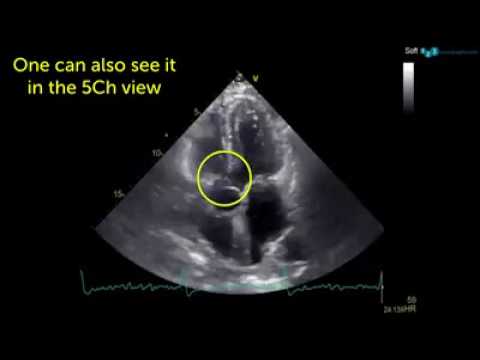



60 Sec Case Roots Sinus Valsalva Aneurysm Youtube




Supplemental Materials For Thrombosed Aneurysm Of The Left Sinus Of Valsalva Presenting As An Intramyocardial Mass Journal Of The American Society Of Echocardiography




How To Master Aortic Measurements With These 5 Techniques




Transthoracic Echocardiography Confirming Right Coronary Sinus Of Download Scientific Diagram




Transcatheter Closure Of Type I Ruptured Right Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Damara Sr Barik R Akula S Nig J Cardiol




Classical Windsock Deformity Of Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva An Unusual Appearance On Transthoracic Echocardiography Bmj Case Reports




Aneurysm Of Sinus Of Valsalva An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Two Dimensional Imaging Of A Complex Three Dimensional Structure Measurements Of Aortic Root Dimensions Journal Of The American Society Of Echocardiography




Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysms A State Of The Art Imaging Review Journal Of The American Society Of Echocardiography




Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Diagnosis By Community Echocardiography In Echo Research And Practice Volume 7 Issue 4




How To Master Aortic Measurements With These 5 Techniques




Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysms Circulation




Back To The Basics Aortic Valve Anatomy




Echocardia Wiki




Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysms A State Of The Art Imaging Review Journal Of The American Society Of Echocardiography




Unruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Obstructing The Left Ventricular Outflow Tract An Uncommon Presentation In Childhood The Annals Of Thoracic Surgery



1



Echocardiography



Scan Views Echocardiografie




Extremely Rare Case Of A Rupture Of The Left Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Into The Main Pulmonary Artery Abstract Europe Pmc




Multiple Ruptured Aneurysm Of Left Sinus Of Valsalva A Rare Entity Sarupria A Kapoor Pm Kiran U Hote M Ann Card Anaesth




Back To The Basics Aortic Valve Anatomy




Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Clinical Case Presentation And Management Parashar Nk Bhasin D Marotrao Ps Farooqui Fa Verma Sk Saxena A J Pract Cardiovasc Sci




Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysms A Review With Perioperative Considerations Journal Of Cardiothoracic And Vascular Anesthesia




Figure 1 From Rupture Of Right Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Into Right Cardiac Chambers The Role Of Different Imaging Modalities Semantic Scholar




Successful Device Closure Of A Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Presenting With Acute Heart Failure Bmj Case Reports




An Extracardiac Unruptured Right Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Complicated With Atherothrombosis In Echo Research And Practice Volume 3 Issue 1 16




Aneurysm Sinus Of Valsalva Dissecting Into Interventricular Septum As Download Scientific Diagram
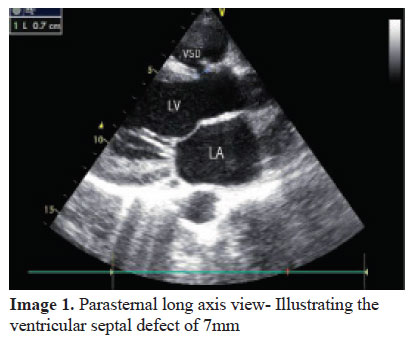



Echocardiographic Diagnosis Of Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva With Congenital Vsd And Ar




Classical Windsock Deformity Of Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva An Unusual Appearance On Transthoracic Echocardiography Bmj Case Reports



コメント
コメントを投稿